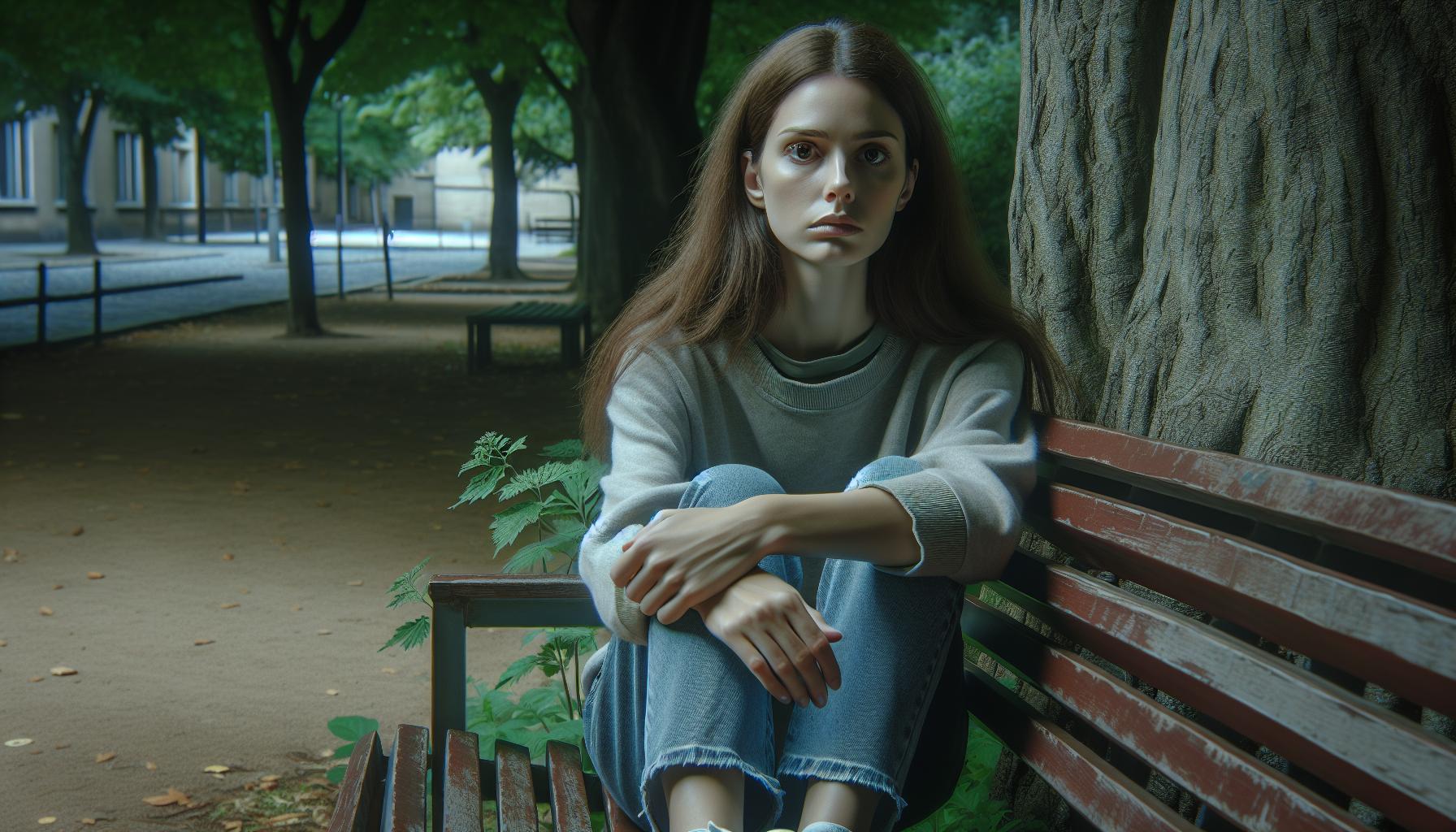
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can have a profound impact beyond physical health. I’ve seen how they can shape emotional and social well-being, often leading to feelings of shame, anxiety, and isolation. Understanding these effects is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of sexual health.
When someone is diagnosed with an STI, it can trigger a cascade of emotional responses that affect relationships and self-esteem. The stigma surrounding STIs can make it difficult to communicate openly with partners and friends. In this article, I’ll explore how STIs influence emotional and social health, shedding light on the importance of awareness and support in overcoming these challenges.
- Impact on Emotional Health: STIs can lead to heightened feelings of anxiety, depression, shame, and isolation, affecting overall emotional well-being.
- Stigma and Shame: The stigma associated with STIs often exacerbates feelings of shame and self-blame, hindering open communication and support-seeking.
- Social Isolation: Individuals with STIs may withdraw from social activities due to fear of judgment, which can worsen feelings of loneliness and emotional distress.
- Communication Struggles: An STI diagnosis can strain relationships and hinder effective communication, leading to misunderstandings and emotional distance between partners.
- Importance of Support: Engaging in support networks, such as peer groups or professional counseling, can help mitigate emotional and social challenges related to STIs.
- Coping Strategies: Seeking professional help and discussing feelings with trusted individuals can facilitate emotional healing and foster resilience in managing the consequences of STIs.
Which of The Following Best Describes The Effects of an STI on Emotional and Social Health?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) significantly affect both emotional and social health. Following an STI diagnosis, individuals often experience a range of emotional responses, such as shame, anxiety, and fear. These feelings can lead to decreased self-esteem and increased social isolation. The stigma surrounding STIs exacerbates these emotional challenges, making it harder for individuals to seek support.
Social interactions can also suffer. Relationships may become strained due to fear of transmission or judgment from partners, friends, or family. This strain can manifest as withdrawal from social activities or reluctance to engage in new relationships.
Awareness of the effects of STIs on emotional and social health plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges. Support networks, including healthcare professionals and peer groups, can provide vital assistance. Seeking help offers individuals a chance to discuss feelings and receive the emotional support needed to navigate the consequences of an STI effectively.
Emotional Effects of STIs
which of the following best describes the effects of an sti on emotional and social health?. Understanding these effects is crucial for managing emotional responses effectively.
Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression often accompany an STI diagnosis. Many individuals experience worry about health outcomes and potential transmission to partners. This concern may lead to chronic stress, triggering feelings of unease. Depressive feelings can emerge, characterized by sadness, hopelessness, or a lack of motivation. Research indicates that STIs contribute to increased depressive symptoms among affected individuals, influencing their overall quality of life. Managing these emotions and seeking support can make a significant difference in emotional well-being.
Stigma and Shame
Stigma and shame frequently arise with an STI diagnosis. People often fear judgment from others, which exacerbates feelings of isolation. This stigma can prevent individuals from discussing their experiences or seeking help. Shame may manifest as self-blame or negative self-perception, further damaging self-esteem. Studies show that the stigma associated with STIs can hinder recovery and emotional healing. Open conversations can help reduce stigma and promote empathy, fostering an environment of support and understanding.
Social Health Implications
STIs significantly impact social health, influencing interactions, relationships, and overall social dynamics. Understanding these implications is crucial for fostering supportive environments.
Relationships and Communication
Effective communication often suffers after an STI diagnosis. Partners may struggle to discuss feelings, concerns, or health-related issues. This lack of communication can lead to misunderstandings, mistrust, and emotional distance. I recommend honest dialogues about health status and feelings, which can strengthen relationships and enhance mutual support. Strengthening communication skills in intimate relationships fosters connection and reduces anxiety, creating a more open atmosphere for discussing sexual health.
Social Isolation
Social isolation frequently occurs alongside an STI diagnosis. Individuals might withdraw from social circles due to stigma or fear of judgment. This withdrawal can intensify feelings of loneliness and decrease overall emotional well-being. Engaging in support networks can counteract this isolation. Seeking peer support groups or counseling offers safe spaces for expressing feelings and experiences. Building connections with others facing similar challenges nurtures a sense of belonging and reduces the emotional burden of STIs.
Coping Mechanisms
Coping with the emotional and social effects of STIs involves leveraging support systems and seeking professional assistance. These strategies significantly enhance individual well-being and foster resilience.
Seeking Support
Engaging with trusted friends or family can provide a sense of safety and understanding. Discussing feelings and concerns opens avenues for emotional relief and connection. Peer support groups offer similar benefits, allowing individuals to share experiences and strategies for coping with an STI diagnosis. These groups create a judgment-free environment where members can discuss fears and anxieties. Active participation in such networks fosters camaraderie and diminishes feelings of isolation.
Professional Help
Consulting with healthcare professionals plays a vital role in emotional healing. Professionals provide valuable information, counseling, and resources tailored to individual needs. Therapy can address anxiety, depression, and relationship strain associated with STIs. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and group therapy both offer constructive approaches to processing emotions and developing coping strategies. Seeking professional help promotes a holistic approach to emotional and social health, encouraging proactive engagement with one’s mental well-being.
Effects of STIs
which of the following best describes the effects of an sti on emotional and social health? I’ve seen how a diagnosis can create a ripple effect that impacts self-esteem and relationships. It’s crucial to address the emotional turmoil that comes with an STI to foster healing and connection.
Building a support network can significantly alleviate feelings of shame and isolation. I believe that open conversations about STIs can break down stigma and create an environment where individuals feel safe to share their experiences. By prioritizing emotional well-being and seeking help, we can navigate the complexities of STIs together, ultimately enhancing our overall quality of life.